Sea lice set to survive increased ocean acidification

The strain of sea louse most closely linked to the spread of disease and mortalities in both farmed and wild Atlantic salmon is unlikely to be adversely affected by the increasing acidification of the oceans.
L. salmonis appears to be equipped with mechanisms that will allow it to cope with the increasingly acid nature of the oceans
So suggest the authors of a new study, which tested whether Lepeophtheirus salmonis could cope with increased partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2) - one of the water quality concerns associated with ocean acidification.
This strain of louse is a major pest in salmon aquaculture and, due to its economic impact it is one of the most well studied species of marine parasite. However, as the authors of the study point out, there is limited understanding of how increased concentration of pCO2 will impact host-parasite relationships.
As a result they investigated the effects of three different levels of pCO2 on growth and metabolic rates of the planktonic stages of L. salmonis.
They found that, other than increasing respiration levels, “the treatments did not have a significant effect on the other biological endpoints measured (carbon, nitrogen, lipid volume, and fatty acid content).”
As a result, they conclude, that: “The results indicate that L. salmonis have mechanisms to compensate for increased concentration of pCO2 and that populations will be tolerant of projected future ocean acidification scenarios.”
The full study, published in PeerJ as The planktonic stages of the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) are tolerant of end-of-century pCO2 concentrations, can be accessed here.
Có thể bạn quan tâm
Phần mềm

Phối trộn thức ăn chăn nuôi
Pha dung dịch thủy canh

Định mức cho tôm ăn

Phối trộn phân bón NPK

Xác định tỷ lệ tôm sống

Chuyển đổi đơn vị phân bón

Xác định công suất sục khí

Chuyển đổi đơn vị tôm
Tính diện tích nhà kính
Tính thể tích ao hồ
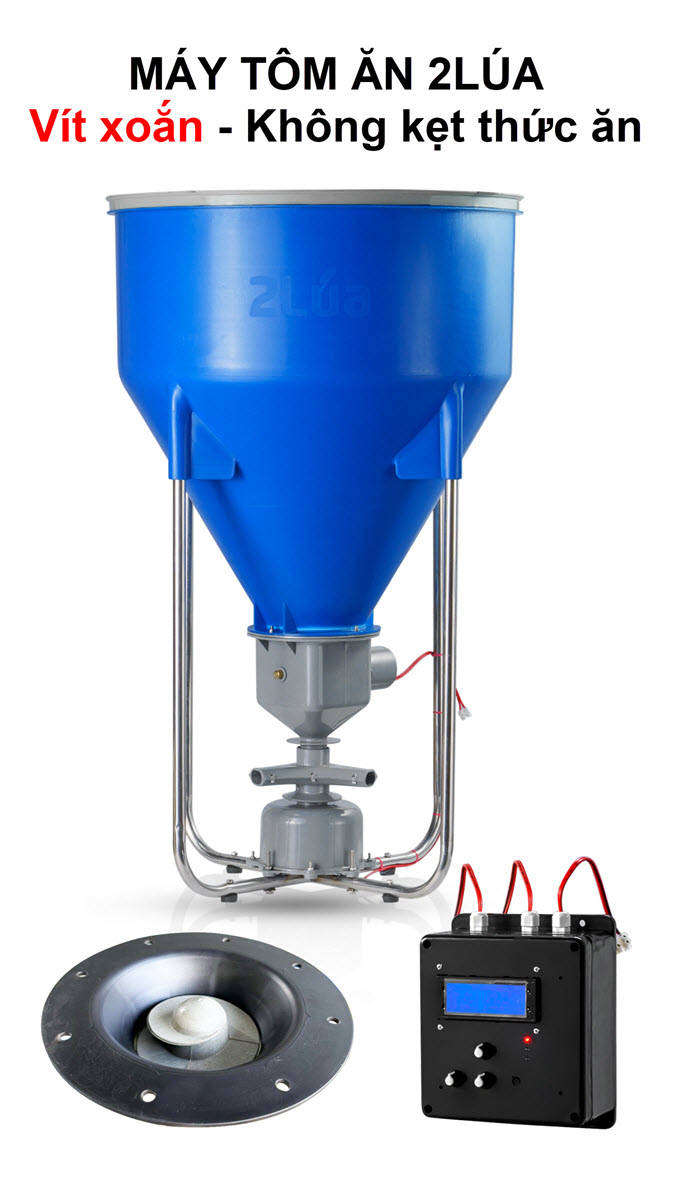




 BioMar’s latest feed diet cuts out cleaner fish…
BioMar’s latest feed diet cuts out cleaner fish…  The US accept the equivalent system: great opportunity…
The US accept the equivalent system: great opportunity…